Antibiotic Exposure and Kidney Stone Disease Across the Life Course SA-PO207
Poster presented at American Society of Nephrology's Kidney Week, November 03 - November 06, 2022 in Orlando, FL, US .
Authors:
Michelle Denburg, Zeyu N Li, Jing Huang, Lauren E Parlett![]() , Kevin Haynes
, Kevin Haynes![]() , John R Asplin, Ingrid Y Luna, Charles Bailey
, John R Asplin, Ingrid Y Luna, Charles Bailey![]() , Gregory E Tasian
, Gregory E Tasian![]()
Presenting author: Michelle Denburg
Abstract
Background
Kidney stone disease (KSD) is increasingly common and associated with considerable morbidity. Antibiotic (ABX) exposure may be a risk factor for KSD.
Methods
We examined the association between 12 classes of oral ABX and KSD in a case-control study nested in the HealthCore Integrated Research Database (HIRD) of longitudinally integrated medical and pharmacy claims from healthcare encounters of members with ≥6 months of continuous enrollment in commercial health plans across the United States from Jan 2006 to Jan 2020. Incidence density sampling was used to match cases 4-65 years of age at initial KSD diagnosis to up to 5 controls on year of birth, index date, pre-index enrollment time, sex, and geographic region. Exclusion criteria were inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, urinary obstruction, bariatric surgery, malignancy, cystic fibrosis, immobility, and neurogenic bladder. Conditional logistic regression models were stratfied at age 18 and adjusted for other ABX use, healthcare utilization, comorbidities, UTI, thiazide and loop diuretics, H2 blockers, proton-pump inhibitors, statins, corticosteroids, and certain anti-epileptic agents.
Results
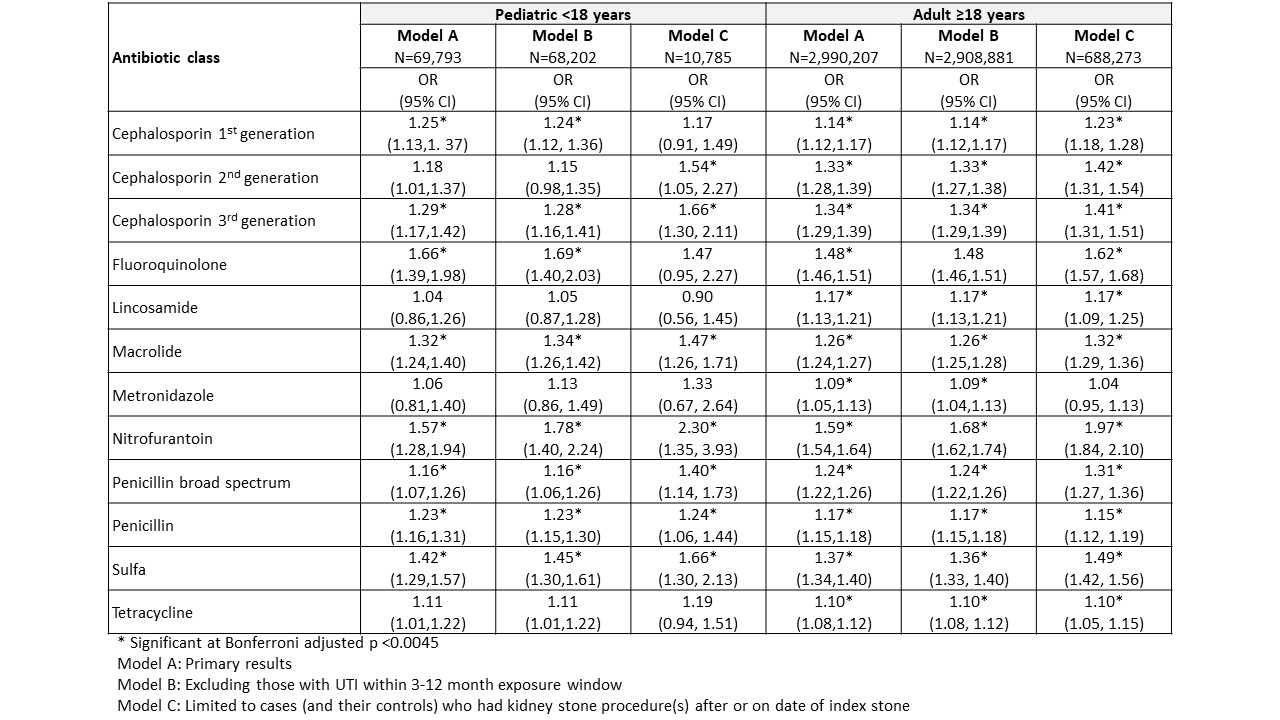
69,793 children (11,622 cases/58,171 controls; 59.9% female) and 2,990,207 adults (498,393 cases/2,491,814 controls; 43.6% female) were included. Exposure to any of the 12 ABX classes in adults and 8 different ABX classes in children within 3-12 months prior to index was associated with KSD at the Bonferroni adjusted significance threshold (Table). The magnitude of association was greatest for fluoroquinolone, nitrofurantoin, and sulfa ABX with adjusted OR of 1.37-1.66 and similar effect estimates in sensitivity analyses excluding those with UTI during the exposure window and restricting to cases who had KSD surgery on or aftex index and their controls.
Conclusion
Leveraging a large claims database, we confirmed that exposure to oral ABX is associated with KSD diagnosis in children and adults.
Tags
Analytic: conditional logistic regression
Data Source: claims
Research Focus: antibiotics | nephrology
Study Design: case-control
Funding Transparency
This work was possible through:
- Grant/Award
Additional details:
- Tasian - NIH - 5R01DK122156 : Evaluation of the gut-kidney axis in kidney stone disease
Entry last updated (DMY): 25-01-2025.